Crop Production and Management
Crop Production and Management
- All living organisms require food.
- The energy from food is utilised by an organism for carrying out its various life processes such as digestion, respiration and excretion.
- Plants can make their food themselves but animals including humans cannot.
- We get our food from plants or animals, or both.
In our country three categories of crops are grown:
- Kharif Crops: The crops which are grown in the rainy season (i.e., from June to September) are called Kharif crops. Paddy, maize, soybean, groundnut, and cotton are Kharif crops.
- Rabi Crops: The crops are grown in the winter season (i.e., from October to March) are called rabi crops. Examples of rabi crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard, and linseed.
- Zaid Crops (or Summer Crops): The crops grown in the summer season are ( called zaid crops. Moong, muskmelon, watermelon, cucumber, gourd and bitter gourd are examples of zaid crops.
Cultivation of crops involves the following activities:
- Soil Preparation: It involves loosening and tilling of the soil (i.e., ploughing and watering).
- Sowing: Sowing is the process of putting seeds in the soil.
- Adding Manure and Fertilisers: The substances, which are added to the soil in the form of nutrients to improve the production of the crops and fertility of the soil are called manure and fertilisers.
- Irrigation: Supply of water to crops at appropriate intervals is called irrigation.
- Protection from Weeds: Weeds are the unwanted plants that grow along with the crops. Its removal is a must for the better growth of the crops. These can be controlled by spraying certain chemicals, called weedicides, like 2, 4-D.
- Harvesting: The cutting of the crop after it is mature is called harvesting.
- Storage: If the crop grains are to be kept for a longer time, they should be safe from moisture, insects and rats.
Humus: Humus is the top layer of the soil formed by decaying or decomposition of organic matters like animal remains, shed leaves, the dung of cattle.
Pests: Pests are the insects or rodents that destroy’much of our crop yield. Thus, it is necessary to save crops from pests.
Important agricultural tools:
Plough: This is used for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds, scraping of soil, etc. This implement is made of wood and drawn by a pair of bulls.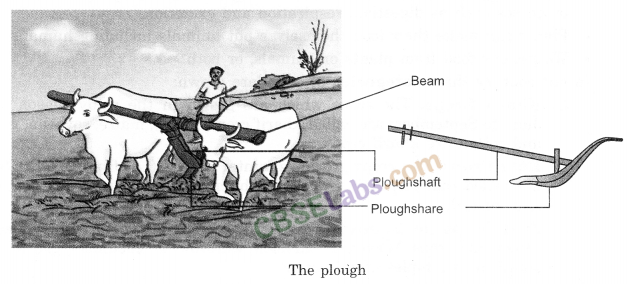
Hoe: It is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil.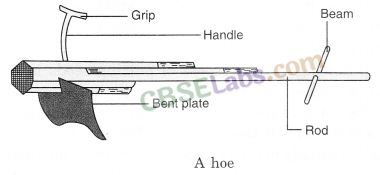
Cultivator: Used for ploughing. It is driven by a tractor. Use of cultivator saves labour and time.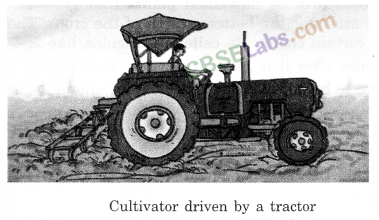
Weeds: Some undesirable or unwanted plants may grow naturally along with the crop, such plants are called weeds.
Weedicides: Those certain chemicals which are used to control weeds are called weedicides. For example 2, 4-D (2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid), metolachlor.
Winnowing: A process to bring out the separation of grain and chaff is called winnowing.
Comments
Post a Comment